Last Update: Nov. 15, 2025
This assignment focuses on text processing, file input, and file processing. It will use methods in the StdDraw class.
Due: 11:55 PM, Sunday, November 23, 2025
IMPORTANT: The best advice we can give you about PS6 is to carefully test, debug, and re-test your code as you write it. Do not attempt to write a whole program at once—if you do, then you may have no idea where to find the error if the program doesn't work. Proactive testing will save you enormous amounts of time in the long run. Trust us!It is said that the XMU College experience is to keep yourself busy, really busy, with many tasks. The objective of Part 2 is to help you, by writing a program that displays the remaining time to each future task, and the elapsed time from each past-due task.
4 PS5 | 11/16/2025 11:55:00 PM Exam 1 | 1/1/2025 11:35:00 AM PS6 | 11/23/2025 11:55:00 PM Winter | 1/11/2025 8:00:00 AM
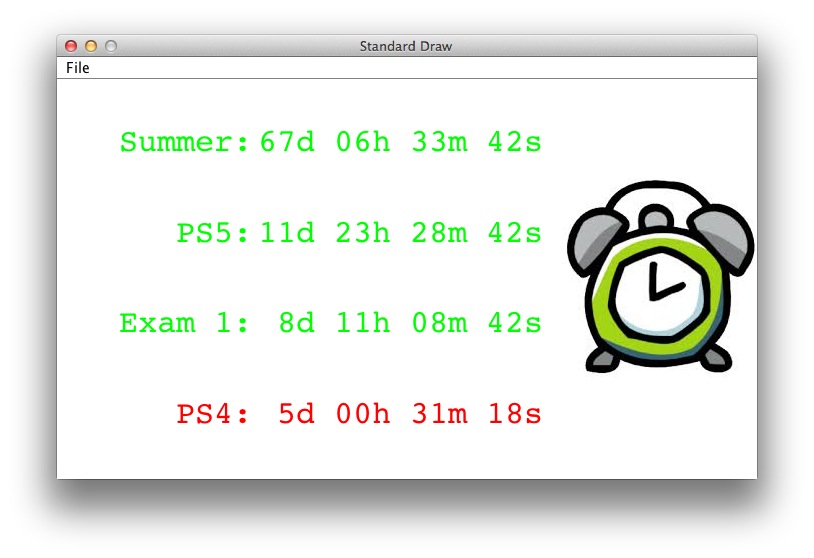
Starter code: TaskMan.java. You are more than welcome to change it in any way you want. We discuss a few key points:
One issue you need to resolve is to parse each line representing a task into two pieces: task name and task deadline string. You can use the substring/indexOf method, or split. An example of using split is:
String string = "123-456789";
String[] parts = string.split("-");
String part1 = parts[0]; // 123
String part2 = parts[1]; // 456789
If you see extra space at the end of a string, you can use the trim() method of String.
We use Integer.parseInt( The sample code uses the GregorianCalendar class to convert time
with multiple components to a much simpler representation commonly
used in Computer Science called the Epoch time, i.e., time starting
from the beginning of 1970. To use GregorianCalendar, the sample code has:
Below is a code segment to represent the example PS6 time:
Note that since GregorianCalendar counts month from 0, one uses 0
for January, 1 for February, etc.
The sample code uses an infinite loop:
Some Suggestions.
Remember the top-down design and
bottom-up implementation strategy we covered in class?
You might want to make it a milestone to extract task time
and test it with multiple inputs until it works before you move to the
next step.
You may make a next milestone to implement and test
if time is valid, which will involve defining other methods such as
determining the number of days in a month.
Another suggested milestone will be
converting from second to the day/hour/min/sec representation.
Please submit electronically for assignment #6 and make sure you
submit (1) TaskMan.java. Please be sure that you choose the
.java file,
NOT the .class file when uploading. The .class file is the compiled version of your code which we cannot
examine and grade. So, please make sure you submit *.java files. Also, remember that you always
need
to include the header. The submission repository for ps6 is https://gitee.com/simmonsong/ct-xmuf25-ps6.
Please follow the instructions in Assignments Submission to submit your assignments. Git introduction is a help document for git
utilization.. Enjoy!
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
GregorianCalendar event = new GregorianCalendar(2016, 2, 6, 23, 55, 0);
// convert to milliseconds from EPOCH
long eventTimeMS = event.getTimeInMillis();
for ( ; ; )
{
// get current time from EPOCH in millisecond
long currentTimeMS = System.currentTimeMillis();
// compute difference between currentTimeMS and eventTimeMS
// and compute the display
// sleep 1 second and then clear
}
Part 3: Submit Your Assignment
//*******************************************************************
//
// File: FileName.java Assignment No.: 6
//
// Author: <your name> Email: <your email>
//
// Class: ClassName
//
// Time spent on this problem:
// --------------------
// Please give a description about your design.
//
//*******************************************************************
Some part of the problem set derived from Building Java Programs.